Single Layer PCB Vs Multi Layer PCB – Advantages, Disadvantages, Design and Manufacturing Process.
Before designing a printed circuit board, you must decide whether to use a single-layer or multi-layer PCB. Both types of design are used in many everyday devices. The kind of project you are using the board for will determine which one is best for you. Multi-layer boards are more common for complex devices, while single-layer boards can be used for simpler devices. This article will help you understand the differences and choose the right type for your project.
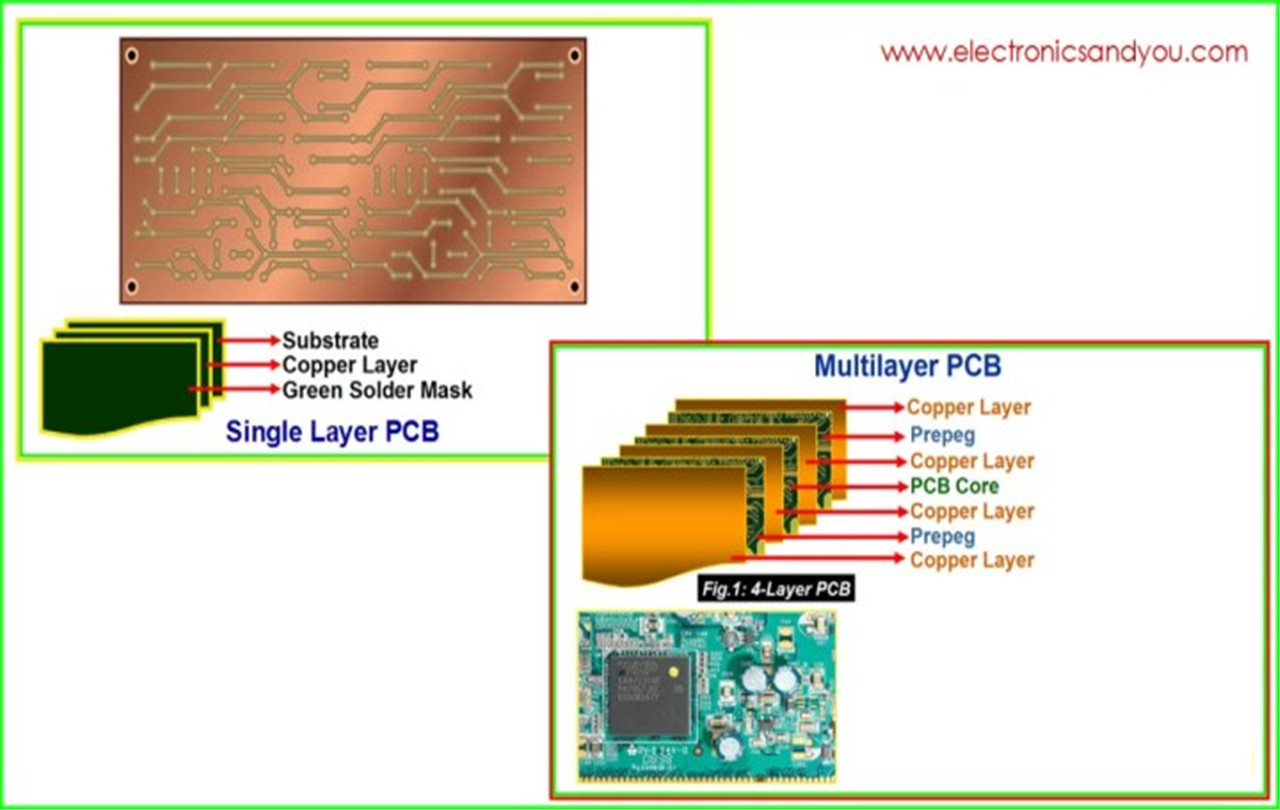
Based on the names of these PCBs, you can probably guess what the difference is. A single-layer board has one layer of base material (also known as a substrate), while multi-layer boards contain multiple layers. When examining them closely, you'll notice many differences in how these boards are constructed and function.
If you’re interested in reading more about these two PCB types, then continue reading!
What is Single Layer PCB?
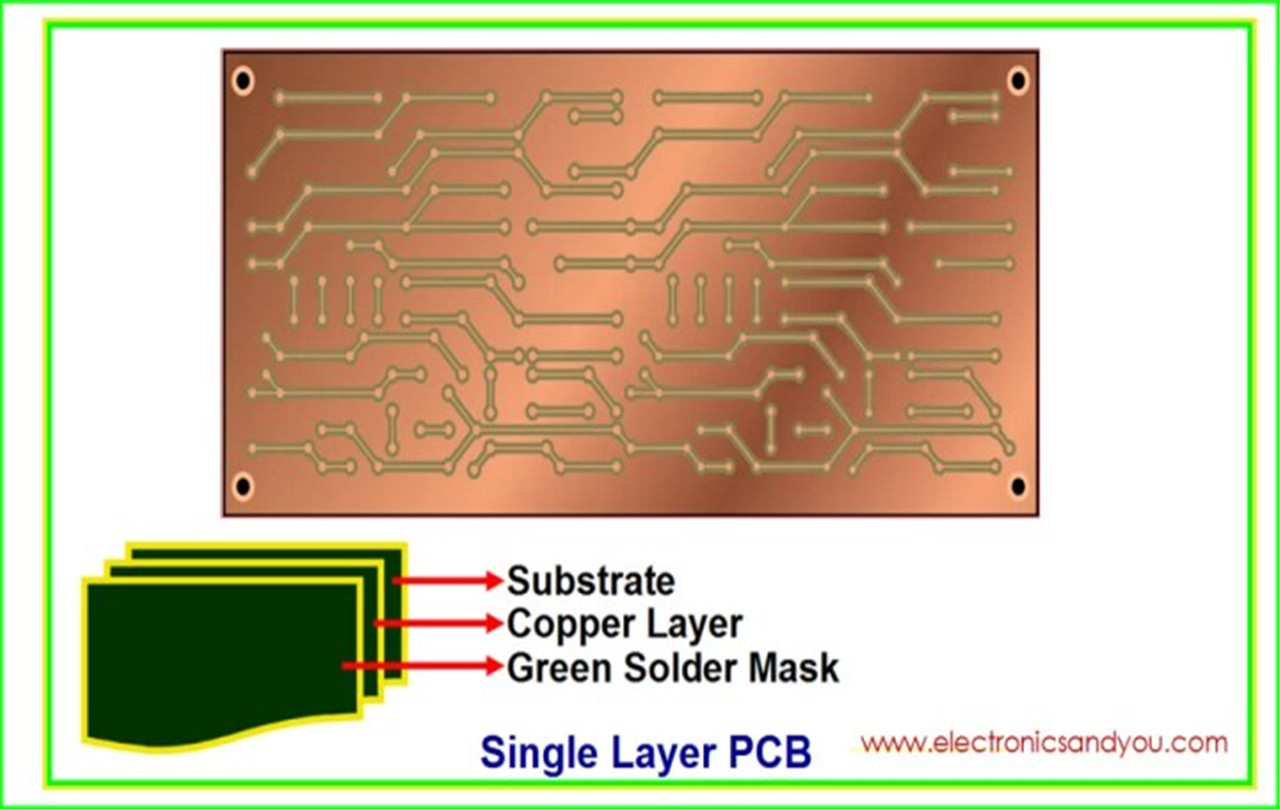
Single-sided boards are also known as single-sided boards. They have components on one side and a conductor pattern on the other. These boards have one layer of conductive material (typically copper). A single-layer board consists of a substrate, conductive metal layers, a protective solder layer, and a silk screen. Single-layer boards are found in many simpler electronic devices.
Advantages of Single Layer PCB
1. Inexpensive
Overall, a single-layer PCB is less costly due to its simplistic design. That’s because it can be developed in a time-efficient manner without relying on a large number of PCB material. Plus, it doesn’t require much knowledge.
2. Quickly Manufactured
With such a simple design and low-resource reliance, single-layered PCBs can be manufactured in no time! Of course, that’s a huge advantage, especially if you need a PCB as soon as possible.
3. Easy to Produce
The popular single-layer PCB can be designed without technical difficulties. That’s because it offers a simple design process so manufacturers and professionals can produce them without problems.
4. You can order in Bulk
Because of their easy development process, you can order plenty of these PCB types at the same time. You can even expect to see a drop in costs per board if you order in bulk.
Disadvantages of Single Layer PCB
1. Limited Speed and Capacity
These circuit boards offer minimal options for connectivity. That means that the overall power and speed will diminish. Additionally, the operational capacity decreases as a result of its design. The circuit may not function for high-power applications.
2. It does not offer much Space
Complex devices will not benefit from a single-layer circuit board. That’s because it offers very little space for extra SMD Components and connections. Wires coming in contact with each other will cause the board to operate improperly. The best practice involves assuring that the circuit board provides sufficient space for everything.
3. Larger and Heavier
You will need to make the board larger to provide additional capabilities for various operational purposes. However, doing this will also increase the product’s weight.
Application of Single Layer PCB
Because of their low manufacturing cost, single-sided boards are popular in many household appliances and consumer electronics. These are popular for devices that can store little data. Some examples include:
● Coffee makers
● LED lights
● Calculators
● Radios
● Power Supplies
● Varying Sensor Types
● Solid State Drives (SSD)
What is Multilayer Layer PCB?
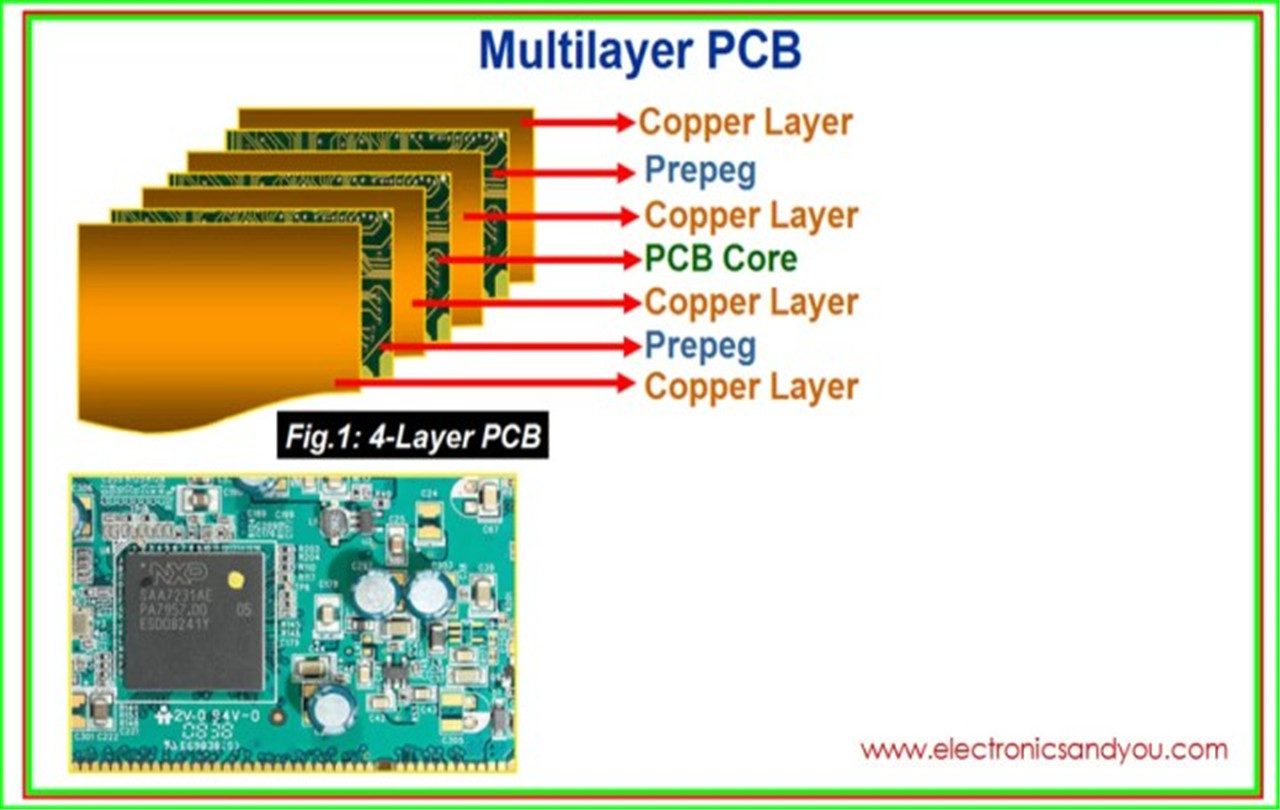
Multi-layer PCBs consist of multiple double-sided boards stacked on top of one another. They can have as many boards as needed, but the longest one made was 129-layers thick. They typically have between 4 and 12 layers. However, unusual amounts can lead to problems like warping or twisting after soldering.
A multi-layer board's substrate layers have a conductive metal on each side. Each board is joined using a specialized adhesive and an insulating material. The multi-layer boards have solder masks at the edges.
Advantages of Multilayer Layer PCB
1. Complex Projects
Complex devices relying on additional components and circuits usually need a multi-layer PCB. You can expand the board via additional layer integrations. This makes it suitable for additional circuits that feature extra connections, which otherwise won’t fit on a standard board.
2. More Durable
Additional layers increase the board’s thickness, making it durable. This will then ensure longevity and allow it to survive unexpected events, including drops.
3. Connection
Several components would usually need more than one connection point. In this case, a multi-layer PCB only needs an individual connection point. Overall, this advantage contributes to the device’s simple design and lightweight features.
4. More Power
Adding more density to a multi-layered PCB makes it practical for power-intensive devices. Generally, this means it can operate more quickly and efficiently. The increased capacity makes it suitable for powerful devices.
Disadvantages of Multilayer Layer PCB
1. More Expensive
You can expect to pay more with a multi-layered circuit board since it requires additional materials, expertise, and time to develop. For this reason, you should ensure that using a multi-layer component is more advantageous than the price.
2. Lengthy Lead Time
Multi-layer boards will take longer to develop. This is due to essential parts that require locking so that each layer will form an individual board. Each of these processes contributes to the overall completion time.
3. Repairs can be Complex
If a multi-layered PCB experiences problems, then it can be difficult to repair. Some internal layers may not be viewed from the outside, making it harder to pinpoint what’s causing component or physical board damages. Plus, you will need to consider the number of integrated components on the board because it makes the repairs more difficult to complete.
Difference: Single Layer PCB Vs Multi Layer PCB
1. Manufacturing Process
A single layer PCB undergoes a lengthy manufacturing process. Typically, it involves using many CNC machining processes to create the board. The entire process involves cutting-drilling-graphics placement-etching-solder mask and printing.
Afterward, it goes through surface treatment before being tested, inspected, and packaged for shipping.
Meanwhile, multilayer PCBs are created through a special process. It involves overlaying prepreg and foundational material layers together through high pressure and temperature. This ensures that air won’t become entrapped between each layer. Also, it means that resin will cover the conductors and the adhesive securing each layer together melts and cures correctly.
2. Material
Single-layer and multi-layer PCBs are manufactured using metal, FR-4, CEM, Teflon, and polyimide materials. Even then, copper is the most common choice.
3. Cost
Overall, the single-layer PCB is less costly than a multi-layer PCB. That’s mainly because of the materials used, time to produce, and expertise. Other factors may affect the price, including size, lamination, lead time, etc.
4. Application
Generally, single-layer PCBs are used for simple devices, while multi-layer PCBs are more applicable for advanced technology, such as smartphones.
Deciding whether you need single-layer or multi-layer PCBs
It would help if you determined whether multi-layer or single-layer printed circuit boards are required for your project. Then, consider which type of project you have and what the best fit is. These are the five questions you should ask yourself:
1. Which level of functionality will I require? You may need more layers if it is more complex.
2. What is the maximum board size? Multi-layer boards allow for more functionality in a smaller area.
3. Do you value durability? Multi-layer is the best option if durability is a priority.
4. How much do I have to spend? Single-layer boards are best for budgets that are less than $500.
5. What is the lead time for PCBs? The lead time for the single-layer printed circuit board is shorter than that of multi-layer boards.
Other technical questions, such as operation frequency, density, and signal layers, will need to be addressed. These questions will determine whether you require a board with one, three, four, or more layers.
Post time: Feb-14-2023
