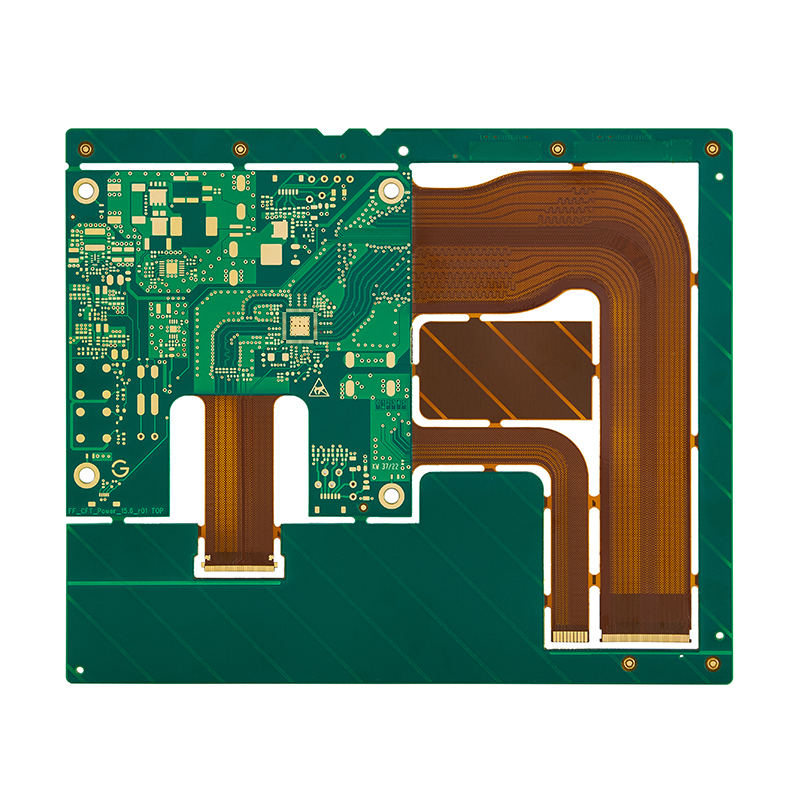
Custom 4-layer rigid flex PCB
Product Specification:
| Base Material: | FR4 TG170+PI |
| PCB Thickness: | Rigid: 1.8+/-10%mm, flex: 0.2+/-0.03mm |
| Layer Count: | 4L |
| Copper Thickness: | 35um/25um/25um/35um |
| Surface Treatment: | ENIG 2U” |
| Solder Mask: | Glossy green |
| Silkscreen: | White |
| Special Process: | Rigid+flex |
Application
Pacemakers, cochlear implants, handheld monitors, imaging equipment, drug delivery systems, wireless controllers, among others. Applications – Weapons guidance systems, communication systems, GPS, aircraft missile-launch detectors, surveillance or tracking systems, and others.
FAQs
A: As the name implies, a rigid flex PCB is a combination of both rigid and flexible substrates. One or more flexible circuits are used to connect subcircuits on rigid PCBs.
The base material used in most common rigid printed circuit boards is woven fibreglass impregnated in epoxy resin. It’s actually a fabric, and although we term these “rigid” if you take a single laminate layer they have a reasonable amount of elasticity. It’s the cured epoxy which makes the board more rigid. Because of the use of epoxy resins, they are often referred to as organic rigid printed circuit boards. The most common material choice used as a flex PCB substrate is polyimide. This material is very flexible, very tough, and incredibly heat resistant.
It is lightweight and compact, hence, reduced packaging size. It can be designed to fit confined or smaller areas, contributing largely in product miniaturization. It can be bent and folded easily to fit perfectly into smaller devices.
The production process of Flex-rigid PCB boards are numerous, the production is difficult, the yield is low, the pcb materials and manpower wasted more. Therefore, the price is relatively expensive and the production cycle is relatively long.
1. For small order, we usually use EXPRESS shipping to ensure the timely delivery, such as FedEx, DHL, UPS, TNT,etc.,
2. For mass production, we usually use air economy or sea or track shipping to save your cost.
3. If you have your own forwarder, we can also ship the goods by your forwarder.
Rigid-flex PCBs is a complicated product that demands a lot of interaction between our and your technicians. Like other complex products, early discussions between Lianchuang Electronics and the designer is necessary to optimize the design for manufacturability and to optimize costs.
Available structures for rigid flex PCBs
There are numerous, different structures available. The more common ones are defined below:
Traditional rigid flex construction (IPC-6013 type 4) Multilayer rigid and flexible circuit combination containing three or more layers with plated through holes. Capability is 22L with 10L flex layers.
Asymmetrical rigid flex construction, where the FPC is situated on the outer layer of the rigid construction. Containing three or more layers with plated through holes.
Multilayer rigid flex construction with buried / blind via (microvia) as part of the rigid construction. 2 layers of microvia are achievable. Construction may also include two rigid structures as part of a homogeneous build. Capability is 2+n+2 HDI structure.
Please contact us if you need further information or assistance, we are happy to help you.